There is a risk of worm infection or even leaving home. Various worms can be found in household items, banknotes, tableware, food, and drinking water.
Parasites enter the human body in a convenient way: they can enter the digestive system through food, water, dirty hands or being bitten by insects.
In addition, worms can affect certain internal organs, use human resources, cause mechanical damage and actively multiply. Their life course is accompanied by unpleasant and often dangerous symptoms and damage to various organs.
How to identify intestinal worms
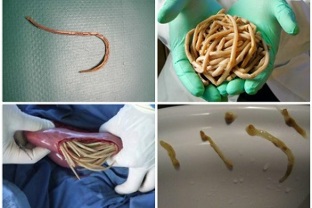
Intestinal helminthiasis combines a group of diseases caused by different types of worms. The most common are as worm disease (roundworm), intestinal helminthiasis (pinworm), hookworm disease (hookworm). These parasites live in the human intestinal cavity and feed on their contents. Their existence can be suspected by many characteristic symptoms:
- Significant weight loss effect, no need to change diet and physical activity. Intestinal worms use human nutrition as a source of energy for growth and reproduction. The devices (pumping unit, fish hook) they fix in the intestine can damage their walls and interfere with the absorption of other trace elements.
- The movement of worms, the mechanical damage caused by the movement of worms, and the release of larvae or adults from the body into the external environment can cause stomach, belly button, and rectal itching.
- Various digestive diseases: diarrhea or constipation, flatulence, mucus, foam or blood in the stool, nausea, vomiting. In some cases, adult parasites can be found in the stool.
Signs of parasites in the liver
A large number of nutrients accumulate in the human liver, and strong blood circulation occurs, which is very convenient for parasites. Common liver helminthiasis: fascial helminthiasis, aspirin worm disease, scleroderma, caused by flukes.
You can identify them by specific functions:

- The sharp pain in the lower right cartilage is caused by the mechanical action of the worm. Therefore, Echinococcus forms cysts in the organs and tissues, causing the development of inflammatory processes and even necrosis.
- Adult worms (roundworms) can block the bile ducts, which can interfere with the flow of bile, the digestion process in the body is difficult, and the patient will show signs of jaundice. The visible mucosa of humans is yellow, and the skin is also stained as the pathology develops. The non-specific symptoms of the appearance of zx parasites will be deterioration of general physical condition, weight loss, nausea, and lethargy.
To clarify the diagnosis, they donated blood for analysis. Leukocytosis and eosinophilia were detected, and biochemical tests showed increased activity of liver enzymes (ALT, AST). During the ultrasound examination, liver damage is visible in the body: swelling, inflammation, and in some cases parasitic cysts.
What indicates the presence of lung worms
Some parasites (roundworm, Toxoplasma gondii, Echinococcus chinensis, Tworm) can enter the blood or lymph flow of the human lungs from the gastrointestinal tract. They multiply in the alveoli, making breathing difficult, and certain species (Echinococcus) form cysts, destroying the structure of the organs.
Because the symptoms are similar to respiratory diseases with viral and non-communicable causes (bronchitis, ARVI), it is difficult to determine whether there are parasites in the lungs. Coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fever indicate the need for further examination of the patient's body.
Blood-borne parasites
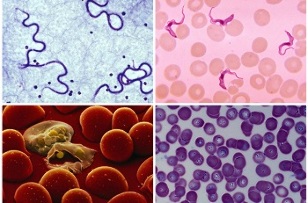
Protozoan single-celled worms can be found in the lumen of blood vessels. Babesia, plasmodium (Plasmodium), trypanosomiasis, microfilariasis, and schistosomiasis can cause dangerous diseases that endanger human life.
They destroy the forming elements, disrupt the energy metabolism process in the body, and hinder the supply of nutrients to organs and tissues.
In most cases, human infections occur after being bitten by insects or worms. After some time, signs of anemia appear in the body: pale, then mucous membranes, dizziness, sudden weight loss and deterioration of health. Without timely medical services, parasites in the blood can seriously threaten human life.
Diagnosis involves a microscopic examination of the blood. During this process, you can find single-celled parasites and damaged red blood cells, as well as determine the type of worm. Treatment is long-term, fixed treatment under the guidance of qualified doctors.
Abnormal habitat of parasites
Certain types of worms can penetrate the human heart, subcutaneous tissue (wireworm), brain and spinal cord (cysticercus, Echinococcus occidentalis). Not only in a foreign country, but also by eating familiar foods that have not been properly heat-treated, they can be infected, and pets can become carriers. The signs of invasion depend on the degree of damage to a particular organ.
In the brain, worms form cysts, which are fibrous formations that cause neurological phenomena.
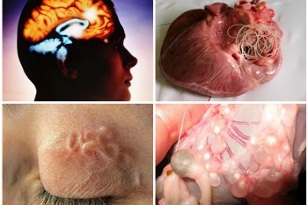
Headache of unknown etiology, tremor of limbs, changes in tactile sensitivity, impaired motor coordination, sharp deterioration of hearing and vision-signs of development of invasion depend on the location of the worm and its larvae.
Adults can be seen under the skin, usually accompanied by itching and tingling, as well as in the eyes, ear canal, and other places.
What to do if you see signs of a worm infection
After all necessary examinations have been performed and the type of parasite has been determined, the cause of the parasite should be treated under medical supervision. Prescribe anthelmintics with a narrow or wide range of action for restorative and symptomatic treatment to promote the elimination of worms from the body. In some cases, surgical treatment is required.
If treatment is started on time, the prognosis for most diseases will be good. If you delay seeing a doctor or start taking medication on your own, the treatment process may be delayed, and many types of parasites can damage vital organs or body systems, and even cause death.



























